Laser Welding Copper with Blue High Power Diode Laser
445 nm wavelength and 6 kW laser power (CW) for laser welding of copper, gold and other non-ferrous metals.
To the examples445 nm wavelength and 6 kW laser power (CW) for laser welding of copper, gold and other non-ferrous metals.
To the examplesThe blue laser enables controlled laser welding of copper and other non-ferrous metals with low material thickness. Whereas thin foils were previously cut rather than joined with an infrared laser, the blue laser can now be used to process the material in a targeted and controlled manner. Thanks to its high absorption in copper, the blue laser allows for significantly improved process stability, especially when working with electrical contacts, battery components as well as thin sheets and foils. The blue laser light is used to melt the desired material along the joints. The molten copper solidifies cleanly, forming weld seams with excellent mechanical strength and electrical conductivity. The liquefied metal melts flow into each other and form the weld seam as they cool. This process produces particularly smooth seams that are of excellent quality and therefore highly stable. In addition, minimal heat distortion and a narrow heat affected zone contribute to a high surface quality of the welded components and reduce changes to the material surface. The process is basically the same as with an infrared laser radiation – apart from the wavelength used.
With industrial laser beam sources available to date, it was only possible to process non-ferrous metals such as copper successfully in series production with increased effort. Thanks to recent advances in laser technology, particularly the development of high-power blue diode lasers, laser welding of copper and gold has become significantly more efficient and reliable. These materials absorb the blue light spectrum seven to twenty times better than infrared light (see graphic), which dramatically improves energy coupling and melt behavior in the infrared range.
The blue high power diode laser significantly improves the laser welding process of non-ferrous metals. Thin foils and sheets, in particular, can be processed much more effectively with the blue laser, enabling higher welding speed, deeper weld penetration and better weld quality even on thin materials. But the blue diode laser offers even more advantages.


In addition to the high absorption of blue light, which makes it much easier to melt copper, the use of the intensity profile characteristic of diode lasers also contributes to the top-notch processing outcome. This focused beam profile ensures a stable melt pool, high beam quality and precise control of the laser parameters during the welding process. Furthermore, Laserline's proven diode laser technology allows the high laser power to be finely graduated within milliseconds, thus adapting it perfectly to the process requirements and optimizing the power density and laser energy input. This also helps reduce the formation of copper oxides and ensures stable processing despite material surface variations and surface tension effects. The weld seams created during welding copper are extremely clean and very smooth – regardless of the surface quality of the material before the welding process was begun. They have excellent electrical conductivity and produce little to no spatters on adjacent areas of the material. This results in minimal rework and reduced contamination risks for surrounding electronic components.
Material efficiency is also particularly high, as the blue laser, on the one hand, does not require any overlap or material reinforcement in the seam area, and on the other hand, liquid copper has a high gap bridgeability for processing with blue laser radiation. The high thermal conductivity of copper is no longer a limiting factor, thanks to the high energy density of the blue laser beam. The option of controlled heat conduction welding enables copper to be used as the upper joining component when welding dissimilar materials for the first time. Even pure copper powder and very thin copper foils can be joined to other materials, such as steel and aluminum. When it comes to welding foils, considerable results have already been achieved in butt and edge welding – and in some cases, even with deep penetration welding.
For users, the LDF and LDM platform provides a familiar and industrially proven system that can be used in conjunction with processing optics optimized for the wavelength. This modular setup enables fast integration and minimal process downtime, making it ideal for implementing high-power laser welding systems in existing production environments. Otherwise, only a few modifications are needed to integrate the laser into production. The sight protection windows of processing cells and protective goggles are the only aspects that have to be replaced, due to the changed wavelength range, in order to meet laser safety requirements for the employees carrying out the work.
In comparison to green laser light or fiber lasers, blue diode lasers offer significant advantages for welding highly conductive and reflective materials such as copper.
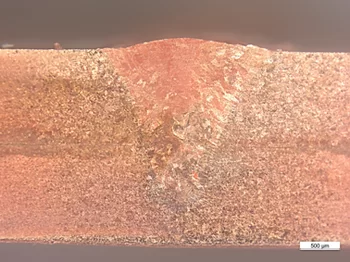
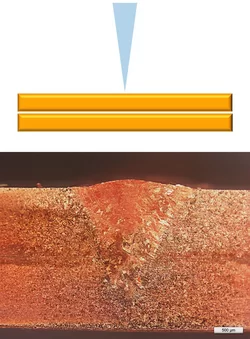
1 to 3 mm copper

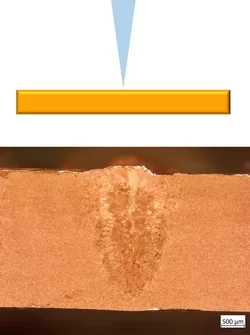
0.8 to 1.5 mm copper

3 mm copper sheet
1 mm copper sheet
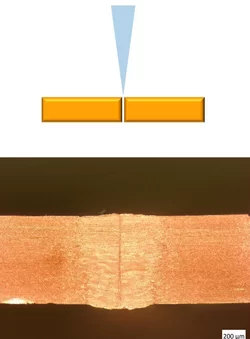
1.2 on 1.2 mm copper sheet

1.2 on 1.2 mm copper sheet
Small motors used in various components of motor vehicles often require precise and reliable welded joints. Copper welding with a blue diode laser can be used in various areas of the automotive sector, e.g. in the manufacturing of electrical motors, sensors, control elements and battery systems.
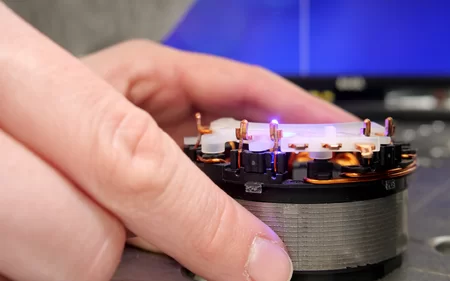
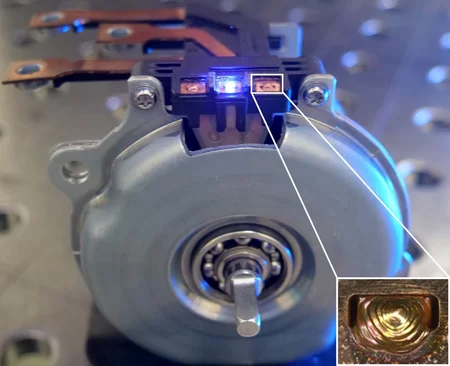
- Welding of three copper contacts on the flattened side of the pins (Pin through sheet)
- Pin: 1 x 2.2 mm²
- Sheet: 1 mm
- Blue Diode Laser LDFblue 3000-30
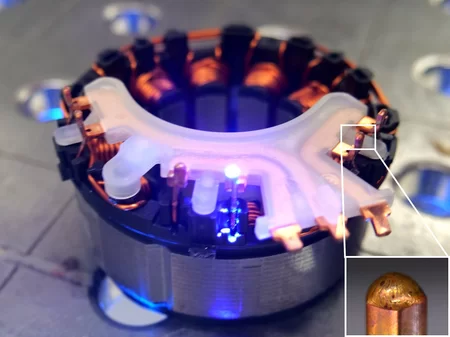
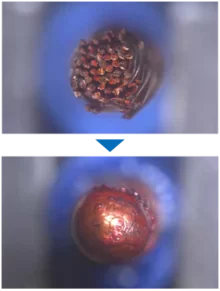
- Welding of six Pins (Pin to Wire)
- Pin: 1 x 1 mm²
- Wire: Ø 0.9 mm
- Blue Diode Laser LDMblue 1800-30
The high absorption capacity of the blue diode laser is advantageous for a wide range of applications and materials, not just copper. Different materials with different properties can be combined without reducing the quality of the weld seam.
Typical material mixtures:
- Special coatings, e.g. gold, nickel
- Material mix, e.g. steel, copper
- Other materials, e.g. steel, titanium, non-metals

0.2 mm copper on 0.3 mm nickel plated steel

0.2 mm to 3 mm gold-coated copper
Laser brazing with the blue diode laser enables a precise and tight connection of copper pipes and fittings, for instance. This method is especially suited for applications requiring clean seams and minimal thermal impact on the surrounding material, such as when working with highly reflective materials like copper. The filler material used is a solder with a melting temperature below that of copper. In laser brazing, the heat is applied via a laser spot adapted to the geometry of the component. The homogeneous top hat profile of the blue diode laser ensures uniform heating. As a result, the heat affected zone remains minimal, preserving the surface quality of the copper components and allowing for precise energy input. Only the brazing alloy melts, fills the brazing gap and thus joins the copper components.
- Process temperature > 450°C
- Medium power range, e.g. 0.5 to 1 kW
- Process time of 2 seconds or more
- High flexibility in the geometric design of the joint
- Targeted energy input
- Good automation and controllability

Simple and robust process due to high absorption capacity and large spot size.
Overcomes gaps, misalignments and part tolerances.
4 kW laser power | Hairpins

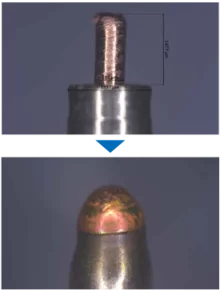
Simple and robust process
High absorption and large spot sizes
Accepts gaps, offsets and component tolerances
Short process times due to immediate melt pool formation
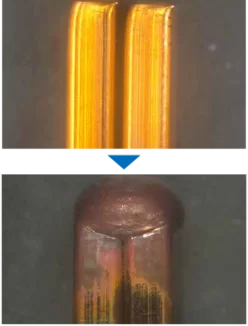
Gap 600 µm
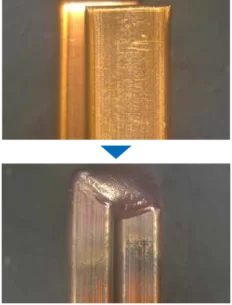
Side offset 1.5 mm
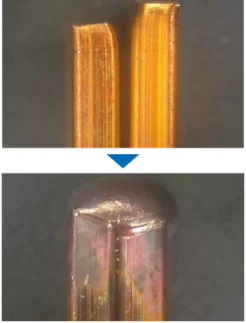
Height offset 1.5mm
The blue diode laser can be used for stripping insulating layers from hairpins. This precise and contactless process ensures the clean removal of insulation while preserving the underlying copper surface. It is necessary in order to enable the subsequent contacting of copper ends. Normally, scanner optics are used. In this process, the laser spot is guided over the defined area, selectively removing the insulation layer in one or more controlled steps.
Which diode laser solutions are especially suitable for laser welding of copper, gold, and other non-ferrous metals with high reflectivity? You can find a selection here.